Indonesia Reports High Human Development Index
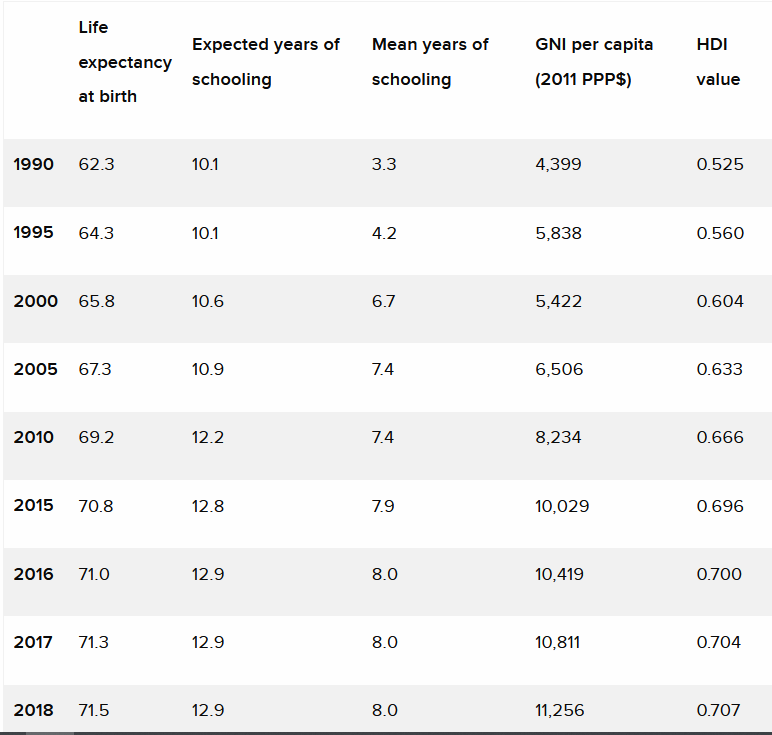
Human Development in Indonesia and its indicators (Source: UNDP Report)
For the first time in the last 20 years, Indonesia has been listed in the group of countries with high Human Development Index (HDI), according to Human Development Report released by the United Nations Development Program (UNDP) on Tuesday (10/12).
“Indonesia’s HDI for 2018 is 0.707, paling the country in the high category of human development, 111th out of 189 countries and regions,” the UNDP report entitled “Beyond Income, Beyond Averages, Beyond Today: Inequality in Human Development in the 21st Century” reads, adding that from 1990 to 2018, Indonesia’s HDI has improved by 34.6 percent from 0.525 to 0.707.
During this period, life expectancy at birth in Indonesia has increased by 9.2 years (from 62.3 to 71.5 years), the average year of schooling has increased by 4.7 years (from 3.3 to 8 years), and the expected years of schooling has increased by 2.8 years (from 10.1 to 12.9 years), while the Gross National Income (GNI) has increased by approximately 155.9 percent (from US$ 4,399 to US$ 11,256).
UNDP representative for Indonesia Christophe Bahuet said that being listed in a group with high HDI was a milestone for Indonesia.
“This achievement is the result of a strong national commitment to boost human development, which not only rests on economic growth but also on the welfare of society, especially health and education,” he said.
The UNDP report also reminded all relevant parties that more optimal efforts are needed in preventing inequality in Indonesia.
According to the UNDP, if inequality is included in the measurement, the Indonesian HDI value could drop 17.4 percent.
Bahuet added that the UNDP report also sent a message to Indonesia for further progress in human development, namely the need to narrow down inequalities and anticipate new gaps in the future.
“The UNDP will continue to be Indonesia’s partner for the progress of human development,” he said.
Translated by: Ridwan Ibadurrohman
Reviewed by: Muhammad Ersan Pamungkas








