National Statistics Agency: Indonesias Human Development Index Increases to 71.39 in 2018
 The National Statistics Agency (BPS) reported that Indonesias Human Development Index (HDI) has managed to reach 71.39 in 2018, or increased by 0.58 point or 0.82 percent compared to the figure in 2017 which stood at 70.81.
The National Statistics Agency (BPS) reported that Indonesias Human Development Index (HDI) has managed to reach 71.39 in 2018, or increased by 0.58 point or 0.82 percent compared to the figure in 2017 which stood at 70.81.
Human development index is measured based on three essential aspects, such as a long and healthy life, knowledge, and decent standard of living. Thus, the increase in HDI is linked to an increase in each aspect, Head of the BPS Suhariyanto said in a press conference, at the BPS Headquartes, Jakarta, Monday (15/3).
The HDI is one vital indicator to measure success in improving quality of human/the people life. The index defines how people can have access to the results of development including income, healthcare, education, and others. For the record, the HDI is introduced by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in 1990 and the methodology and indicators for calculating the index were revised in 2010.
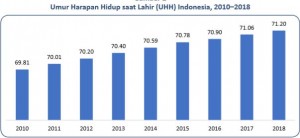
According to Suhariyanto, Life Expectancy at Birth representing long and healthy life continues to increase from year to year. During 2010 to 2018, Indonesias Life Expectancy at Birth increased by 1.39 years or grew by 0.25 percent per year.
In 2010, Life Expectancy at Birth in Indonesia was 69.81 years; the number increased to 71.20 years in 2018, he added.
The second aspect of the HDI is knowledge constituted of two indicators, namely Expected Years of Schooling for Children, and Years of Schooling of Population of Ages 25 and over. Based on the data from the Agency, both indicators also showed an increase from year to year.
During a period from 2010 to 2018, Expected Years of Schooling of Children increased by 1.62 years, the Average Years of Schooling also increased by 0.71 years. The increase in Expected Years of Schooling of Children indicates that more Indonesians are attending school, Suhariyanto said adding that Average Years of Schooling in Indonesia reached 12.91 years in 2018 indicating that children who reach school age (7 years old) have the opportunity to complete their education until graduating from high school or Diploma 1 (associate degree).
In addition, the Average Years of Schooling of Population of Ages 25 and over in Indonesia grew by 1.14 percent per year during a period from 2010 to 2018. In 2018 alone, the figure reached 8.17 years- meaning that population of ages 25 and over has completed their education until grade IX. The growth which showing an upward trend is a vital asset for Indonesia to improve its quality of human life.
The last aspect of the HDI is decent standard of living which is reflected by expenditure per capita in which the figure reached Rp11.06 million per year in 2018.
For the last eight years, Indonesias expenditure per capita increased by 2.00 percent per year, Suhariyanto said.
In regional level, Human Development Index in all provinces in Indonesia also showed an increase in the period from 2017 to 2018. During this period, there were three provinces with the fastest human development progress, namely Papua Province (1.64 percent), West Sulawesi Province (1.24 percent), and West Papua Province (1.19 percent).
The progress of human development in Papua Province is driven by education aspect, while the progress in West Papua and North Sulawesi Province are driven by decent standard of living and both aspects respectively, Suhariyanto concluded. (National Statistics Agency PR/ES)
Translated by : Rany Anjany Subachrum
Edited by : Mia Medyana








